|
Use of CI Scale
|
|
|
 Multiplication problems can be
solved very efficiently using the CI scale in conjunction with the D scale. The CI scale
is exactly the same as the C scale except that it has been turned end for end, and
consequently reads from right to left. Multiplication problems can be
solved very efficiently using the CI scale in conjunction with the D scale. The CI scale
is exactly the same as the C scale except that it has been turned end for end, and
consequently reads from right to left.
|
|
|
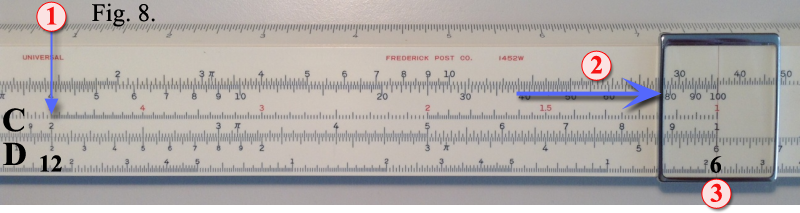
 To multiply using the CI and
D combination of scales, refer to the setting in Figure 9 for the solution of the
problem 6 × 3.33 = 20. To multiply using the CI and
D combination of scales, refer to the setting in Figure 9 for the solution of the
problem 6 × 3.33 = 20.
|
|
|
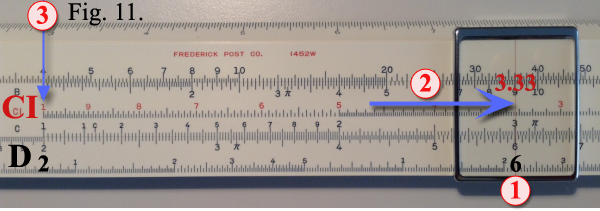
 With the cursor hairline set over
6 on the D scale, draw the slide to bring 3.33 on the CI scale under the hairline.
Under the left index on the CI scale, we find the slide rule answer 2 on the D scale.
Example shown in Figure 11. With the cursor hairline set over
6 on the D scale, draw the slide to bring 3.33 on the CI scale under the hairline.
Under the left index on the CI scale, we find the slide rule answer 2 on the D scale.
Example shown in Figure 11.
|
|
|
 To locate the decimal point, we take
as round figures 6 × 3 = 18. Our answer, therefore, is 20. To locate the decimal point, we take
as round figures 6 × 3 = 18. Our answer, therefore, is 20.
|
|
|
|
Multiplying More Than Two Factors
|
|
|
 The CI–C–D
scale combination is particularly useful in solving multiplication problems involving
more than two factors. For example: Find the volume of a wall 15.5 feet long by 8 feet
high by 0.55 feet thick. The CI–C–D
scale combination is particularly useful in solving multiplication problems involving
more than two factors. For example: Find the volume of a wall 15.5 feet long by 8 feet
high by 0.55 feet thick.
|
|
|
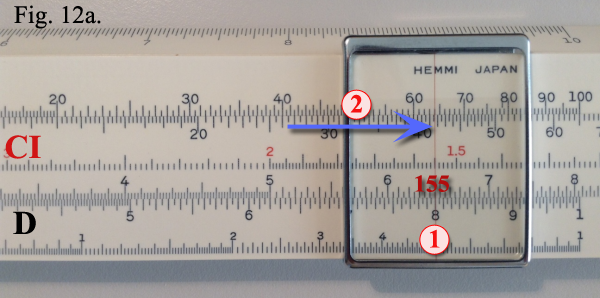
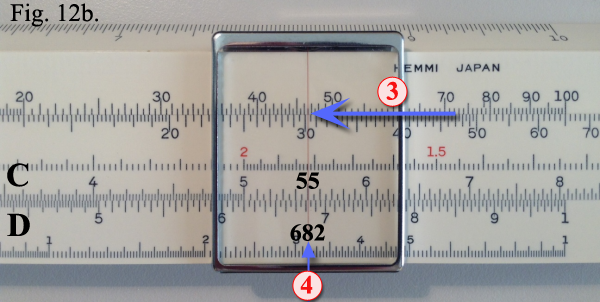
 Solution: Set the cursor hairline
over 8 on the D scale. Set the slide to bring 155 on the CI scale under the hairline.
Example shown in Figure 12a. Now set the hairline over 55 on the C scale. Read 682 under
the hairline on the D scale. Example shown in Figure 12b. Solution: Set the cursor hairline
over 8 on the D scale. Set the slide to bring 155 on the CI scale under the hairline.
Example shown in Figure 12a. Now set the hairline over 55 on the C scale. Read 682 under
the hairline on the D scale. Example shown in Figure 12b.
|
|
|
 To locate the decimal point solver
mentally: 15 × 8 × .5 = 15 × 4 = 60. The correct answer, therefore, is
68.2 cubic feet. To locate the decimal point solver
mentally: 15 × 8 × .5 = 15 × 4 = 60. The correct answer, therefore, is
68.2 cubic feet.
|
|
|
 Notice that in the above
example only one setting of the slide is necessary to solve two multiplications
simultaneously. The partial answer 124, from 8 × 15.5 is on the D scale under the
left index on the C scale. Since the second step in the problem is to multiply by 0.55,
it is necessary only to set the hairline to 55 on the C scale and read the answer, 68.2,
on the D scale without any regard to the partial answer. Notice that in the above
example only one setting of the slide is necessary to solve two multiplications
simultaneously. The partial answer 124, from 8 × 15.5 is on the D scale under the
left index on the C scale. Since the second step in the problem is to multiply by 0.55,
it is necessary only to set the hairline to 55 on the C scale and read the answer, 68.2,
on the D scale without any regard to the partial answer.
|
|
|
|